Applied research

Our research projects are carried out in collaboration with national and international businesses in the EU region of Arnhem and Nijmegen and beyond. ISB has 125 partner universities in Europe, Asia, Latin America and North America, connecting us to SMEs in the Arnhem region and rest of the world.
CIBR as a "Living Lab"
The CIBR aims at offering a living lab context where professionals and organizations can design, experiment and test innovative solutions that forge successful transitions to sustainability.
Together with partners, we co-create pathways to advance ways of thinking and ways of working, to translate insights into actionable steps and implement changes driving new value opportunities.
Our mission is to support organizations to drive meaningful and measurable positive impact in the way international businesses operate for contributing to a more sustainable and equitable world for all.

Knowledge partners and Networks
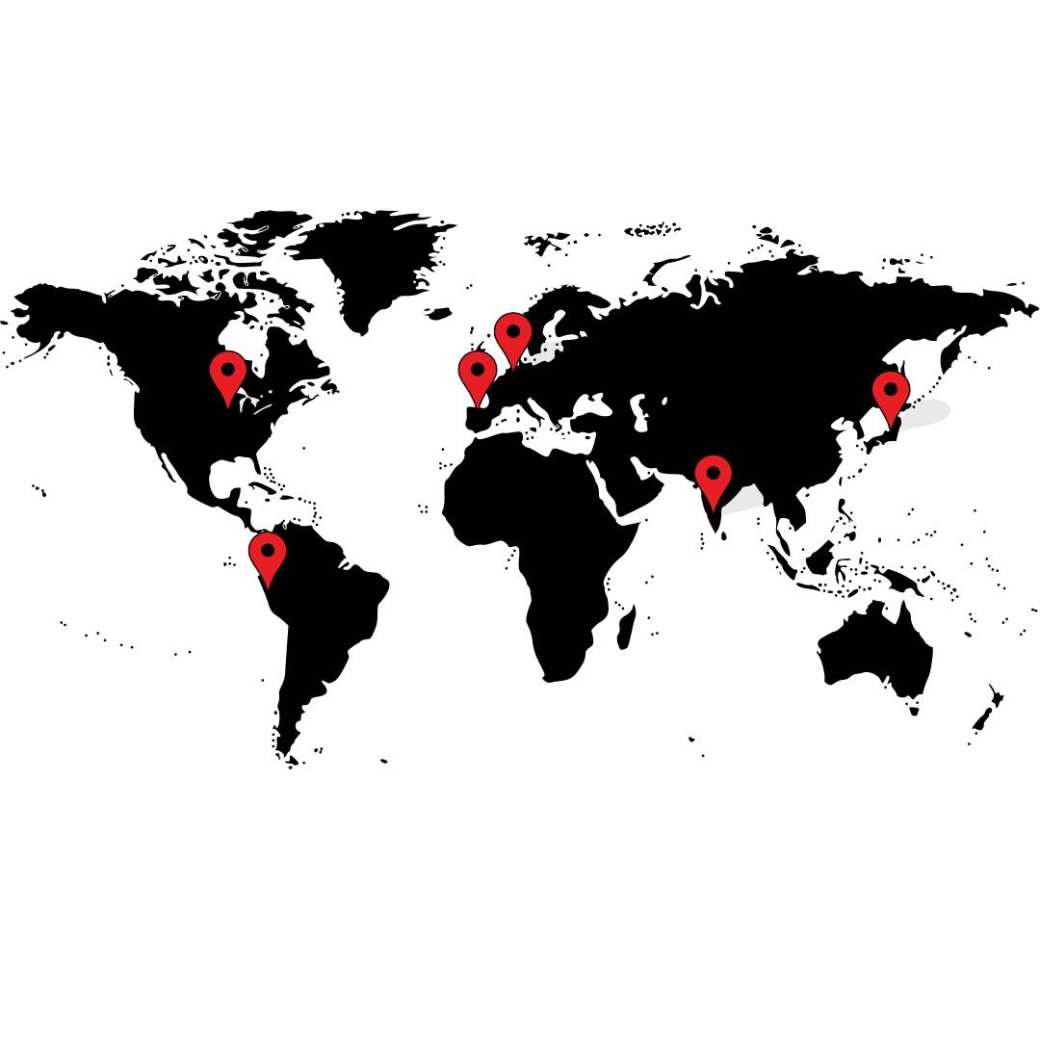
- Wisconsin University Whitewater - USA
- Deusto Business School - Spain
- Akita International University - Japan
- Christ University - India
- ESAN University - Peru
- Peeze koffie - Netherlands
- University of Macedonia - Greece
Projects (will be updated soon)
-
Staff & Output
As a research group, we believe it is important to share our knowledge. This way we deliver a structural contribution to education and educational development. We are pleased to share the results of studies and projects.